Product
Football training for teenagers nutrition and diet
Basic Info
1. Fruits: Fruits are rich in vitamins and trace elements, which can supplement the body's nutrition in various ways and improve the immune system after consumption.
2. Carbohydrates: Common carbohydrates include Mantou, bread, rice, etc. Eating these foods after exercise can quickly supplement and restore energy.
3. Meat: After exercise, the body will consume a certain amount of fat, which can store energy for the body. If the body's fat percentage is too low, it may affect health. At this time, it is advisable to supplement meat appropriately, such as beef, lamb, etc.
2. Carbohydrates: Common carbohydrates include Mantou, bread, rice, etc. Eating these foods after exercise can quickly supplement and restore energy.
3. Meat: After exercise, the body will consume a certain amount of fat, which can store energy for the body. If the body's fat percentage is too low, it may affect health. At this time, it is advisable to supplement meat appropriately, such as beef, lamb, etc.
Soccer, basketball and other ball sports are intense, varied, long duration, intermittent movement, large oxygen debt, and high requirements for endurance and explosive power. A proper diet helps to perform better in sports. So what exactly is the importance of a proper diet for soccer and other ball sports enthusiasts?
Reasonable meals provide sports fans with appropriate energy, which helps the recovery of physical fitness after exercise, and the recovery of physical fitness depends on the level of the body's energy supply and energy reserves (liver glycogen and muscle glycogen), body fluids, vitamins, trace elements, etc.; appropriate diets and liquid rehydration before, during, and after a match can help sports fans maintain a good state, and can reduce and delay the occurrence of prolonged and strenuous exercise-induced It can reduce and delay the occurrence of exercise fatigue caused by prolonged strenuous exercise.
For different types of sports, the reasonable dietary combinations are also different, for example, for sports with high energy demand, attention should be paid to the intake of food with higher energy density in the diet. For high-explosive exercise, meals are needed to promote the body's metabolism. Physical metabolic rate. Research findings have shown that sports nutrition has a positive effect on exercise capacity and performance.
Therefore, there is a need to provide targeted sports nutrition dietary programs for different types of sports enthusiasts so that participation in higher-intensity and more difficult sports competitions can be more effectively guaranteed.
Female 4200kcal/d, male 4700kcal/d. The energy ratio of three meals a day is also important. The morning and afternoon exercise intensity is high, and breakfast and lunch need to provide sufficient and appropriate energy, protein, vitamins, and minerals. Dinner should generally not be too sumptuous to avoid affecting sleep quality and excessive burden on the gastrointestinal tract. It is recommended that the energy ratio for breakfast, lunch, and dinner be 30%, 40%, and 30%.
Secondly, it is important to maintain an appropriate intake ratio of the three major nutrients.
The "Sports Nutrition Practice Guide" aims to provide professional nutritional dietary guidance for improving sports performance and quickly recovering physical fitness. Based on individual physiological differences and dietary nutrition surveys of football players, a reasonable dietary plan is developed for each individual.
Carbohydrates are easy to digest and can quickly produce energy. Football, a large ball sport, requires a large amount of calories to be consumed during the movement, and these calories are mainly supplied by carbohydrates. Carbohydrates can delay central fatigue, prevent excessive ketone body production, and save protein. It is recommended to choose carbohydrates with a high glycemic index. Moderate intake of sugar before, during, and after exercise can effectively improve athletes' endurance. Carbohydrates are recommended to account for 65% -70% of total energy.
Proteins and amino acids can provide energy, delay and alleviate exercise fatigue. Pay attention to ensuring a rich intake of protein. Protein is a component of the human body's motor system - muscles, and protein deficiency can affect muscle contraction during exercise. At the same time, it is important to avoid excessive protein intake, as prolonged running in football increases oxygen consumption and protein metabolism requires a large amount of oxygen. Excessive protein intake can increase the burden on the liver. It is recommended that football enthusiasts consume 15% -17% of their total energy from protein, with high-quality protein accounting for at least 1/3. Fish, poultry, beef, milk, beans, etc. are all good choices!.
Due to the high intensity of football (85% VO2max), there is an increase in oxygen consumption, glycogen breakdown, and lactate production during exercise, which can inhibit fat breakdown; The acidic metabolites produced by fat breakdown can easily cause sports fatigue and reduce athletes' endurance. Therefore, it is recommended that football enthusiasts consume no more than 20% of their total energy in fat.
Generally speaking, large ball sports such as football consume a lot of energy and undergo significant changes in the internal environment during exercise, resulting in a higher production of lactic acid. You can choose foods rich in alkaline substances in your diet, usually rich in potassium, calcium, sodium, etc. Food has a certain alkalinity, such as vegetables, fruits, beans and their products, which can produce alkaline oxides, effectively neutralize the lactic acid produced by exercise in the body, and relieve fatigue after exercise.
For this type of exercise that requires long-term exercise, strong explosiveness, and high endurance, developing a suitable and personalized diet and hydration plan before, during, and after exercise can effectively improve and maintain exercise ability. Next, we will explain how to develop personalized hydration plans and dietary patterns before, during, and after exercise.
So, how to develop a personalized rehydration plan before, during and after exercise? A review study concluded that formulating a personalized sports rehydration plan based on the impact of exercise on the body's hydration status is more helpful in maintaining the body's appropriate hydration status during exercise and improving exercise ability.
Post-exercise: rehydration volume is equivalent to 125% to 150% of the body's sweat loss.
On the other hand, in addition to the amount of rehydration, the composition of the fluid should also be considered. A daily intake of 140 mL of a solution containing nitrates (about 800 mg) before a competition helps to improve the ability to perform high-intensity intervals and to maintain endurance for prolonged intervals. Supplementation with a 6.4% sugar-containing solution during the race will help prolong sprint times.
Post-race intake of fluids containing protein (0.2 g/kg body weight/h) and sugar (0.3 g/kg body weight/h) promotes protein synthesis in the skeletal muscles of the body, improves the body's protein balance, and facilitates physical recovery.
What are the principles of developing a personalized dietary pattern before, during and after exercise that contributes to the improvement of athletic performance? For soccer players with poor physical fitness, the diet needs to be supplemented with abundant glucose and amino acids, especially before matches, and timely replenishment of carbohydrates to increase the individual's anti-fatigue ability and maintain better endurance and explosive power.
During exercise: timely replenishment of body fluids and dilution of fruit juices, food is not recommended.
After exercise: immediately replenish sugar (sugary drinks), 6 hours of regular replenishment of body fluids, at least half an hour to eat after exercise, more carbohydrates for energy, less fat, moderate protein, vegetables and fruits are also essential, fruits contain antioxidants, which help to restore physical energy, avoid overeating.
In summary, the development of personalized and reasonable dietary nutrition plans for soccer and other ball sports enthusiasts is related to their athletic ability and physiological health. Therefore, it is particularly important to provide nutritious and appropriate dietary nutrition for every big ball sports enthusiast!

LDK football product recommendations
The importance of a reasonable diet
Previous domestic studies on the dietary status of soccer and other athletes have found that common nutritional problems include: lack of self-nutritional knowledge, high consumption of energy-supporting substances and insufficient supply, energy intake at three meals, irrational ratios of intake of the three major nutrients, dehydration after profuse sweating, loss of minerals, vitamin deficiencies, and micronutrient deficiencies.Reasonable meals provide sports fans with appropriate energy, which helps the recovery of physical fitness after exercise, and the recovery of physical fitness depends on the level of the body's energy supply and energy reserves (liver glycogen and muscle glycogen), body fluids, vitamins, trace elements, etc.; appropriate diets and liquid rehydration before, during, and after a match can help sports fans maintain a good state, and can reduce and delay the occurrence of prolonged and strenuous exercise-induced It can reduce and delay the occurrence of exercise fatigue caused by prolonged strenuous exercise.
For different types of sports, the reasonable dietary combinations are also different, for example, for sports with high energy demand, attention should be paid to the intake of food with higher energy density in the diet. For high-explosive exercise, meals are needed to promote the body's metabolism. Physical metabolic rate. Research findings have shown that sports nutrition has a positive effect on exercise capacity and performance.
Therefore, there is a need to provide targeted sports nutrition dietary programs for different types of sports enthusiasts so that participation in higher-intensity and more difficult sports competitions can be more effectively guaranteed.
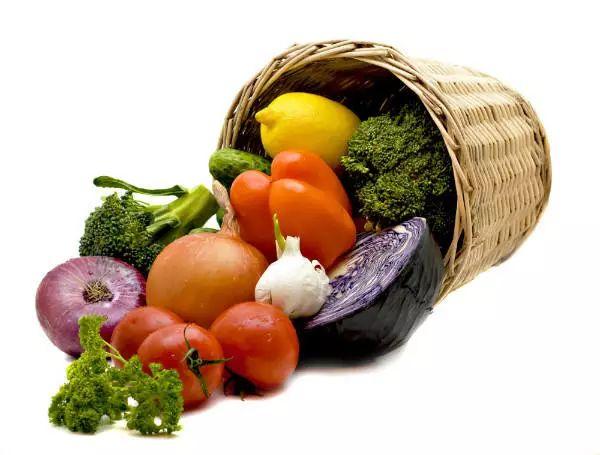

Dietary nutrition recommendations for big ball sports
Firstly, daily energy intake recommendations for football and other ball sports enthusiastsFemale 4200kcal/d, male 4700kcal/d. The energy ratio of three meals a day is also important. The morning and afternoon exercise intensity is high, and breakfast and lunch need to provide sufficient and appropriate energy, protein, vitamins, and minerals. Dinner should generally not be too sumptuous to avoid affecting sleep quality and excessive burden on the gastrointestinal tract. It is recommended that the energy ratio for breakfast, lunch, and dinner be 30%, 40%, and 30%.
Secondly, it is important to maintain an appropriate intake ratio of the three major nutrients.
The "Sports Nutrition Practice Guide" aims to provide professional nutritional dietary guidance for improving sports performance and quickly recovering physical fitness. Based on individual physiological differences and dietary nutrition surveys of football players, a reasonable dietary plan is developed for each individual.
Carbohydrates are easy to digest and can quickly produce energy. Football, a large ball sport, requires a large amount of calories to be consumed during the movement, and these calories are mainly supplied by carbohydrates. Carbohydrates can delay central fatigue, prevent excessive ketone body production, and save protein. It is recommended to choose carbohydrates with a high glycemic index. Moderate intake of sugar before, during, and after exercise can effectively improve athletes' endurance. Carbohydrates are recommended to account for 65% -70% of total energy.
Proteins and amino acids can provide energy, delay and alleviate exercise fatigue. Pay attention to ensuring a rich intake of protein. Protein is a component of the human body's motor system - muscles, and protein deficiency can affect muscle contraction during exercise. At the same time, it is important to avoid excessive protein intake, as prolonged running in football increases oxygen consumption and protein metabolism requires a large amount of oxygen. Excessive protein intake can increase the burden on the liver. It is recommended that football enthusiasts consume 15% -17% of their total energy from protein, with high-quality protein accounting for at least 1/3. Fish, poultry, beef, milk, beans, etc. are all good choices!.
Due to the high intensity of football (85% VO2max), there is an increase in oxygen consumption, glycogen breakdown, and lactate production during exercise, which can inhibit fat breakdown; The acidic metabolites produced by fat breakdown can easily cause sports fatigue and reduce athletes' endurance. Therefore, it is recommended that football enthusiasts consume no more than 20% of their total energy in fat.
Generally speaking, large ball sports such as football consume a lot of energy and undergo significant changes in the internal environment during exercise, resulting in a higher production of lactic acid. You can choose foods rich in alkaline substances in your diet, usually rich in potassium, calcium, sodium, etc. Food has a certain alkalinity, such as vegetables, fruits, beans and their products, which can produce alkaline oxides, effectively neutralize the lactic acid produced by exercise in the body, and relieve fatigue after exercise.
For this type of exercise that requires long-term exercise, strong explosiveness, and high endurance, developing a suitable and personalized diet and hydration plan before, during, and after exercise can effectively improve and maintain exercise ability. Next, we will explain how to develop personalized hydration plans and dietary patterns before, during, and after exercise.

Rehydration regimen
If you play big ball games such as football for a long time, body fluids and minerals will be lost through heavy sweating. Prolonged, intense and rapid exercise will destroy the body's water balance, thereby affecting exercise capacity and physiological health. Rehydration before, during and after exercise can help eliminate imbalances in water and electrolyte balance caused by excessive sweating. For this type of athlete, rehydration before, during and after exercise becomes particularly important!So, how to develop a personalized rehydration plan before, during and after exercise? A review study concluded that formulating a personalized sports rehydration plan based on the impact of exercise on the body's hydration status is more helpful in maintaining the body's appropriate hydration status during exercise and improving exercise ability.
Taking football players as an example, the general rehydration plan before, during and after exercise:
Before exercise:
Replenish fluids at a rate of 5-7 mL/kg body weight 4 hours before exercise. If the athlete's urine is darker in color and lower in volume during this period, supplement fluids at a rate of 8-10 mL/kg of body weight 2 hours before exercise.During exercise:
Adjust fluid replacement as needed, generally not exceeding 800 mL/hour total. The recommended fluid replacement during exercise is 50-70% of sweat loss.Post-exercise: rehydration volume is equivalent to 125% to 150% of the body's sweat loss.
On the other hand, in addition to the amount of rehydration, the composition of the fluid should also be considered. A daily intake of 140 mL of a solution containing nitrates (about 800 mg) before a competition helps to improve the ability to perform high-intensity intervals and to maintain endurance for prolonged intervals. Supplementation with a 6.4% sugar-containing solution during the race will help prolong sprint times.
Post-race intake of fluids containing protein (0.2 g/kg body weight/h) and sugar (0.3 g/kg body weight/h) promotes protein synthesis in the skeletal muscles of the body, improves the body's protein balance, and facilitates physical recovery.
What are the principles of developing a personalized dietary pattern before, during and after exercise that contributes to the improvement of athletic performance? For soccer players with poor physical fitness, the diet needs to be supplemented with abundant glucose and amino acids, especially before matches, and timely replenishment of carbohydrates to increase the individual's anti-fatigue ability and maintain better endurance and explosive power.

Before exercise:
Eat 3 hours before the start of exercise, do not eat flatulence or gas-producing food or drinks, eat less easily absorbed high-carbohydrate food, adjust, reduce the protein content of food, prohibit the consumption of food with high fat content, this is due to fat and protein metabolism requires a large amount of oxygen consumption, fat decomposition and metabolism of acid produced by the more likely to induce exercise fatigue.During exercise: timely replenishment of body fluids and dilution of fruit juices, food is not recommended.
After exercise: immediately replenish sugar (sugary drinks), 6 hours of regular replenishment of body fluids, at least half an hour to eat after exercise, more carbohydrates for energy, less fat, moderate protein, vegetables and fruits are also essential, fruits contain antioxidants, which help to restore physical energy, avoid overeating.
In summary, the development of personalized and reasonable dietary nutrition plans for soccer and other ball sports enthusiasts is related to their athletic ability and physiological health. Therefore, it is particularly important to provide nutritious and appropriate dietary nutrition for every big ball sports enthusiast!

More LDK football product recommendations:
Football Cage
Futsal Goals
Metal Football Goal
Aluminum Football Goal
Foldable Football Goal
Portable Football Goal
LDK sports equipment manufacturer's promotion is in progress: Click to contact us now
Futsal Goals
Metal Football Goal
Aluminum Football Goal
Foldable Football Goal
Portable Football Goal